Commercial motor vehicles include buses, delivery trucks, tractor trailers, and vehicles that transport hazardous materials (CMVs). Additional licensing examinations must be passed by CMV drivers in order to obtain a commercial driver’s license (CDL).
A truck’s owner, operator, and CMV carrier confront a slew of obligations every time it hits the road, from ensuring the safety of their drivers and other road users to ensuring the integrity of the cargo being transported. So it’s vital that commercial drivers don’t get behind the wheel after having consumed alcohol or any other drugs that can affect their judgment.
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) mandates post-accident drug and alcohol testing for drivers involved in serious collisions. Because they travel over state lines, carrier vehicles are subject to all applicable traffic regulations at the federal level.
Commercial motor vehicle carriers and their drivers are subject to the following post-accident drug testing rules, which are summarized below. Don’t forget that alcohol tests after an accident use the same procedures. FindLaw’s summary of Commercial DUI Regulations has more information, just like your car accident attorney.
In the aftermath of a car accident, who is subjected to drug testing?
All commercial drivers employed by CMV carriers subject to FMCSA regulations must undergo a pre-employment drug test. Additionally, carriers are required to undertake random drug testing on commercial drivers throughout their employment, and may test drivers who show indicators of impairment. Drivers of commercial motor vehicles (CMVs) may also be tested for drugs after an accident under certain circumstances. The following are a few examples:
Vehicle safety-sensitive behaviors performed by any driver (if the incident resulted in a human death)
Towing may be required for any driver who receives or has received a moving violation citation within 32 hours of an accident involving bodily injury (and that person is treated away from the accident scene by emergency medical personnel).
Post-accident alcohol testing are not exempt from these restrictions. Within eight hours, a test for alcohol must be performed because of how quickly it is broken down.
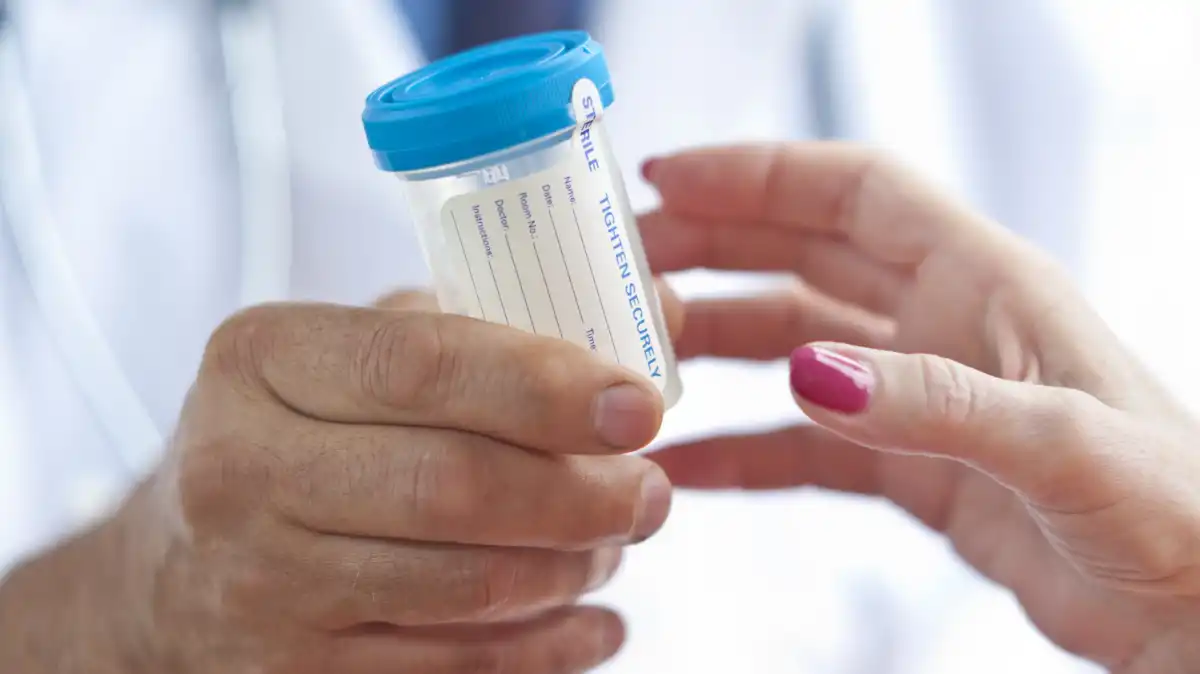
Post-accident drug testing rules and procedures
CMV carriers are obligated to conduct drug testing within 32 hours following an accident since the presence of drugs (via metabolite detection) reduces over time. Carriers must also provide their drivers with information on how to submit to post-accident drug testing before they can operate a vehicle for the business.
As long as the employer obtains the results of urine-based drug tests from federal, state, or municipal officials, they are considered to be in compliance with FMCSA criteria. As long as no additional restrictions have been imposed by law enforcement or there is no reasonable suspicion of impaired driving, carriers may let their staff drivers who have been subjected to post-accident drug testing to continue driving until the results of the test are in.
It’s the responsibility of the carrier/employer to document why a drug test couldn’t be obtained within that time frame. These records must be provided to the FMCSA if requested. It is illegal for drivers to operate CMVs until the return-to-duty process has been properly completed.
CMV Accident Testing Exemptions
Following a CMV accident, there are some restrictions on drug testing. No need to conduct post-accident drug testing that includes:
- Passengers are boarding or alighting from a stationary CMV (exiting).
- Vehicles that are not classified as commercial motor vehicles (CMVs) can be used for cargo loading and unloading.